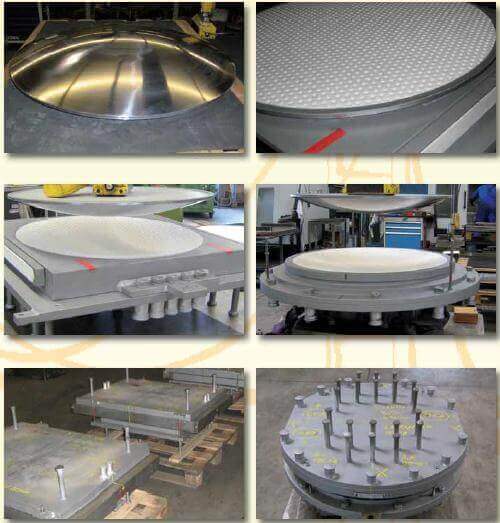
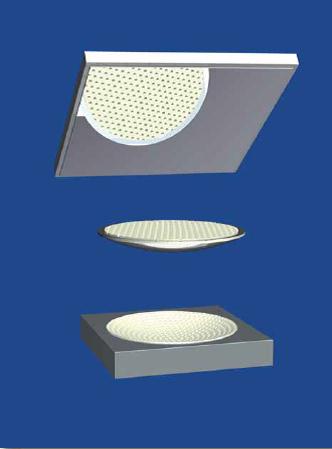
ELA spherical bearings are made of steel, a spherical hard chrome spheroid segment, the so-called convex cup, an appropriate concave captain (PTFE) and a sliding surface on the flat surface of the cap, reinforced PTFE and steel austenitic degree 1.4404.
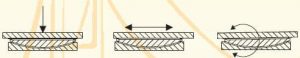
This design is capable of taking up horizontal movements as well as rotation through two independent sliding movements. This fulfills the requirement that structure support should result in very limited restrictions. With guide elements or additional stop rings, it is even more possible to transfer the horizontal load.
Significant for the guy is a relatively compact design and quality, that virtually no vertical movement takes place. This criterion is important for certain applications.
Anchoring to the structure is generally required. If anchoring due to unusual impacts is required, it can be done by additional anchoring plates with appropriate anchoring means.
The standard bearing design does not require anchoring plates for the simultaneous effects of vertical and horizontal loads.
In general, the anchoring methods 3 are the same as the container bearings.
ELA spherical bearings are designed and manufactured in accordance with 1337-5 and are labeled with a relevant CE marking.